Islamic finance is a system of managing money that follows the rules of Islam. It is based on Shariah (Islamic law), which provides guidelines for how Muslims should live their lives, including how they should handle their money.
The goal of Islamic finance is to create a fair and ethical financial system that benefits everyone.
Unlike regular finance, Islamic finance avoids practices like charging or paying interest (riba), gambling, and investing in businesses that are considered haram (forbidden) in Islam.
Instead, it promotes fairness, transparency, and social responsibility. This article will explain the key principles of Islamic finance, the types of financial products available, and how you can start managing your money the halal way.
What is Islamic Finance?
Islamic finance is a way of managing money that follows the teachings of Islam. It is based on the principles of Shariah, which is the Islamic legal system derived from the Quran and the teachings of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH).
Shariah provides rules for all aspects of life, including how money should be earned, spent, and invested.
The main goal of Islamic finance is to create a financial system that is fair and just for everyone. It avoids practices that are considered harmful or unfair, such as charging interest, gambling, and investing in businesses that sell alcohol, pork, or other haram products.
Instead, Islamic finance encourages ethical investing, profit-and-loss sharing, and helping those in need through charity (Zakat).
Islamic finance is not just for Muslims. Anyone who wants to manage their money in a fair and ethical way can use Islamic financial products and services.
Key Principles of Islamic Finance
Islamic finance is based on several key principles that guide how money should be managed. These principles are designed to ensure fairness, transparency, and social responsibility. Here are the main principles of Islamic finance:
- No Riba (Interest):
In Islam, charging or paying interest is not allowed. This is because interest is seen as unfair and exploitative. Instead of earning money through interest, Islamic finance encourages profit-and-loss sharing. This means that when you invest money, you share the profits and losses with the other party. This ensures that both parties are treated fairly. - No Gharar (Uncertainty):
Islamic finance requires that all financial transactions be clear and transparent. There should be no uncertainty or ambiguity in contracts. This means that both parties must fully understand the terms of the agreement and agree to them willingly. - No Haram Activities:
Money cannot be invested in businesses that are considered haram in Islam. This includes businesses that sell alcohol, pork, gambling, or other forbidden products. Instead, Islamic finance encourages investing in halal businesses that benefit society, such as education, healthcare, and halal food. - Zakat (Charity):
One of the key principles of Islamic finance is the concept of Zakat. Zakat is a form of charity that requires Muslims to give 2.5% of their savings to help the poor and needy. This helps reduce poverty and promotes social justice.
Islamic Financial ways
Islamic finance offers a variety of financial ways that follow Shariah rules. These ways are designed to help people manage their money in a halal way. Here are some of the most common Islamic financial ways:
- Murabaha:
Murabaha is a type of Islamic financing that allows you to buy something without paying interest. Instead of taking out a loan with interest, the bank buys the item for you and then sells it to you at a higher price. This higher price includes a profit margin for the bank, but there is no interest involved. - For example, if you want to buy a car, the bank will purchase the car and then sell it to you at a higher price. You can pay for the car in installments over time. This way, you get the car you need without paying interest.
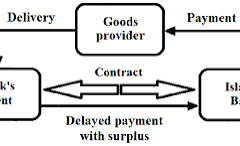
- Mudarabah:
Mudarabah is a type of partnership where one person provides the money, and the other person provides the work. The profits from the business are shared between the two parties according to a pre-agreed ratio. If the business loses money, the loss is shared as well.For example, if you want to start a business but don’t have enough money, you can partner with someone who has the money. You will manage the business, and your partner will provide the funds. You will share the profits and losses according to your agreement. - Sukuk:
Sukuk are Islamic bonds that follow Shariah rules. Unlike regular bonds, which pay interest, Sukuk are based on profit-and-loss sharing. When you invest in Sukuk, you are essentially buying a share in an asset or project. You receive a portion of the profits generated by that asset or project.Sukuk are often used to fund large projects, such as building schools, hospitals, or infrastructure. They are a popular way for governments and companies to raise money in a halal way. - Ijara:
Ijara is a type of Islamic leasing. Instead of taking out a loan to buy something, you rent it from the bank. The bank buys the item and then rents it to you for a fixed period of time. At the end of the lease, you can choose to buy the item or return it to the bank.For example, if you need a car, the bank will buy the car and rent it to you. You will pay rent every month, and at the end of the lease, you can choose to buy the car or return it.
Benefits of Islamic Finance
Islamic finance offers many benefits, both for individuals and for society as a whole. Here are some of the key benefits of Islamic finance:
- Fair and Ethical:
Islamic finance is based on fairness and ethical principles. It avoids practices like charging interest and gambling, which are considered harmful and exploitative. Instead, it promotes profit-and-loss sharing and ethical investing. - Social Responsibility:
Islamic finance encourages social responsibility through the concept of Zakat. By giving 2.5% of their savings to the poor, Muslims help reduce poverty and promote social justice. - Reduces Inequality:
Islamic finance promotes sharing and cooperation, which helps reduce economic inequality. By sharing profits and losses, Islamic finance ensures that everyone is treated fairly. - Encourages Responsible Spending:
Islamic finance encourages people to think carefully about how they use their money. It discourages wasteful spending and encourages investing in things that benefit society.
How to Start Using Islamic Finance
If you want to start managing your money the halal way, here are some steps you can take:
- Learn About Islamic Finance:
Start by learning about the principles and practices of Islamic finance. Read books, take courses, or attend seminars on Islamic finance. - Find Islamic Banks:
Look for banks that offer Islamic financial products and services. Many countries have Islamic banks that follow Shariah rules. - Invest in Halal Businesses:
Make sure your investments are in halal businesses. Avoid businesses that sell alcohol, pork, or other haram products. - Pay Zakat:
Calculate 2.5% of your savings and give it to the poor. You can give Zakat to a charity or directly to people in need. - Avoid Interest:
Avoid taking loans with interest. Instead, use Islamic financial products like Murabaha or Ijara.
Examples of Islamic Finance in Daily Life
Here are some examples of how Islamic finance can be used in daily life:
- Buying a House:
Use Murabaha to buy a house without interest. The bank buys the house and sells it to you at a higher price. - Starting a Business:
Use Mudarabah to start a business. One person provides the money, and the other person does the work. - Saving Money:
Use an Islamic savings account. The bank invests your money in halal businesses and shares the profits with you. - Giving Charity:
Pay Zakat every year. Give 2.5% of your savings to help the poor.
Challenges of Islamic Finance
While Islamic finance has many benefits, it also faces some challenges:
- Limited Options:
There are fewer Islamic financial products compared to regular finance. - Higher Costs:
Islamic financial products can be more expensive. For example, Murabaha may cost more than a regular loan. - Lack of Awareness:
Many people do not know about Islamic finance. They may not understand how it works.
Conclusion
Islamic finance is a way to manage money the halal way. It follows Islamic rules and is fair to everyone. It helps Muslims follow their faith while being good to others. By using Islamic finance, we can make the world a better place.